Network slicing is a virtual networking architecture type that belongs to the software-defined networking (SDN) family and network functions virtualisation (NFV). SDN and NFV allow far better network flexibility through the partitioning of network architectures into virtual slices. Thanks to network slicing multiple virtual networks can be created on top of shared physical infrastructure.
5G wireless technology supports three generic services
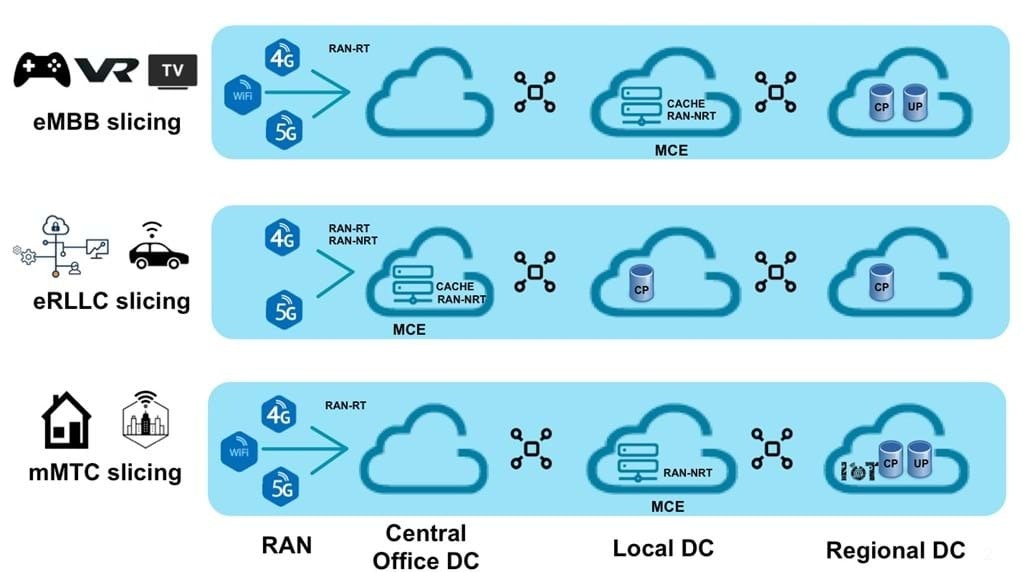
The grand objective of 5G wireless technology is to support three generic services with vastly heterogeneous requirements: enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC). Service heterogeneity can be accommodated by network slicing, through which each service is allocated resources to provide performance guarantees and isolation from the other services. Slicing of the Radio Access Network (RAN) is typically done by means of orthogonal resource allocation among the services.
In this virtualised network scenario, physical components are secondary and logical (software-based) partitions are paramount, devoting capacity to certain purposes dynamically, according to need. As needs change, so can the devoted resources. Using common resources such as storage and processors, network slicing permits the creation of slices devoted to logical, self-contained, and partitioned network functions.
Network slicing and 5G transition
During the 5G transition, 5G systems will be designed in such a way that networks can be sliced on an as-a-service basis. These services can be scaled up and down quickly and easily. Each network slice can be customised to provide the elements necessary for the architecture it requires. For example, 10 percent of a network’s resources can be reserved exclusively for IoT devices.
Additionally, each slice is isolated and comprises the device, access, transport, and core network, thereby increasing reliability and network security. Also, changes and additions to a slice can be made without having to consider the effects across the rest of the network. This saves time, effort, and cost because it takes away the need to re-engineer the whole network with individual slice changes.
Related solutions & services
Our team is ready for you
Do you want to know more about this topic? Leave a message or your number and we'll call you back. We are looking forward to helping you further.